Building Brand Equity is crucial in today’s competitive market, where brands strive to stand out and make a lasting impact. From defining brand equity to discussing strategies and measuring success, this topic dives deep into the world of branding and consumer behavior. Get ready to explore the key elements that shape brand identity and drive consumer loyalty.
Definition of Brand Equity
Brand equity refers to the value a brand holds in the eyes of consumers. It represents the perception of a brand’s reputation, recognition, and overall worth in the market. Building strong brand equity is crucial for businesses as it can lead to increased customer loyalty, higher sales, and a competitive edge in the industry.
Examples of Well-Known Brands with Strong Brand Equity
- Apple: Known for its innovative products, sleek design, and loyal customer base, Apple has built a strong brand equity over the years.
- Coca-Cola: With its iconic logo, consistent branding, and emotional connection with consumers, Coca-Cola is a prime example of a brand with high brand equity.
- Nike: Through its powerful marketing campaigns, endorsement deals with athletes, and focus on quality products, Nike has established a strong brand equity in the sports apparel market.
Impact of Brand Equity on Consumer Behavior and Purchasing Decisions
Brand equity plays a significant role in influencing consumer behavior and purchasing decisions. Consumers are more likely to choose a brand with strong brand equity due to factors such as trust, reliability, and positive associations. Strong brand equity can lead to increased brand awareness, repeat purchases, and advocacy from satisfied customers, ultimately driving sales and profitability for businesses.
Building Brand Equity Strategies
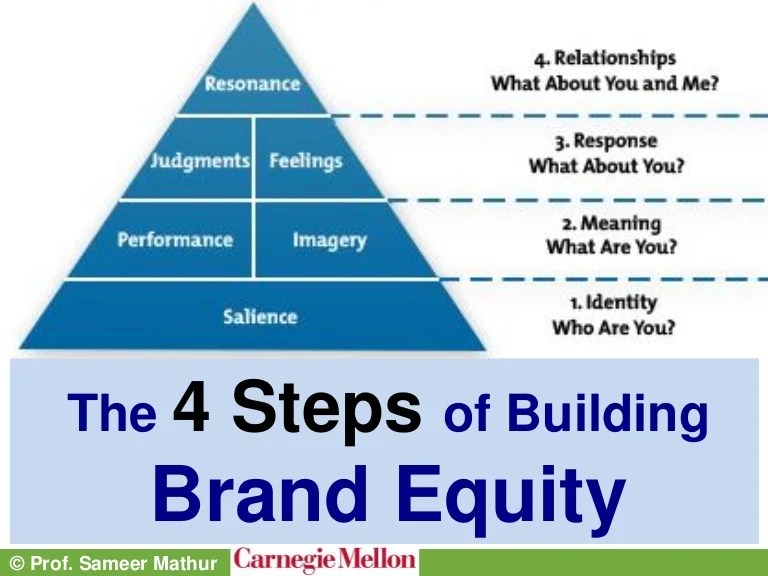
Building brand equity is crucial for companies looking to establish a strong presence in the market and connect with their target audience. There are various strategies that companies can use to build brand equity, whether through short-term tactics or long-term strategies.
Short-term Tactics vs. Long-term Strategies, Building Brand Equity
Short-term tactics for building brand equity often focus on immediate gains and impact, such as promotional campaigns, discounts, or partnerships. These tactics can help boost brand awareness and visibility in the short term. On the other hand, long-term strategies involve creating a strong brand identity, consistent messaging, and quality products or services over time. This approach aims to build trust, loyalty, and a positive reputation among consumers, leading to sustainable brand equity in the long run.
Successful Brand Equity Building Campaigns
One example of a successful brand equity building campaign is Nike’s “Just Do It” slogan, which has become synonymous with the brand’s values of determination, empowerment, and athleticism. This campaign helped Nike establish a strong emotional connection with consumers and differentiate itself from competitors. Another example is Apple’s focus on innovation, design, and user experience, which has created a loyal customer base and a premium brand image in the tech industry.
Brand Identity and Brand Equity: Building Brand Equity
Brand identity and brand equity are closely intertwined concepts in the world of marketing. Brand identity refers to the unique set of brand associations that a company wants consumers to connect with their brand. On the other hand, brand equity is the commercial value that derives from consumer perception of the brand.A strong brand identity plays a crucial role in building brand equity.
When a brand has a clear and consistent identity that resonates with consumers, it can lead to increased brand loyalty, positive brand associations, and higher perceived value. This, in turn, can result in higher sales and market share, ultimately contributing to the overall brand equity.
The Role of Brand Consistency
Brand consistency is key to enhancing brand equity. Consistency in branding elements such as logo, colors, messaging, and overall brand experience helps to create a strong and cohesive brand identity. When consumers consistently encounter the same brand elements across different touchpoints, it reinforces brand recognition and trust.
- Consistent brand identity builds brand recognition: When consumers see consistent branding elements, they are more likely to remember and recognize the brand.
- Strengthens brand loyalty: Consistency in brand messaging and experience fosters trust and loyalty among consumers, leading to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth.
- Increases perceived brand value: A consistent brand identity conveys professionalism and reliability, enhancing the perceived value of the brand in the eyes of consumers.
Measuring Brand Equity
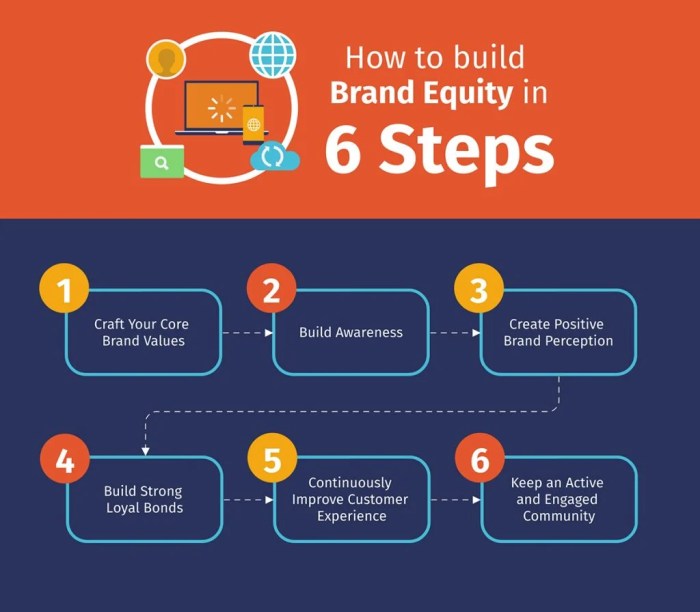
To determine the effectiveness and value of a brand, various methods are used to measure brand equity. These methods provide insights into how well a brand is performing in the market and the perception of consumers towards the brand.
Quantitative Methods
- Surveys: Conducting surveys with target audiences to gather feedback on brand awareness, perceptions, and loyalty.
- Financial Analysis: Analyzing financial data such as revenue, profit margins, and market share to assess the brand’s financial performance.
- Market Research: Utilizing market research techniques to track brand performance against competitors and market trends.
Qualitative Methods
- Focus Groups: Organizing focus group discussions to understand consumer attitudes, emotions, and behaviors towards the brand.
- Brand Audits: Evaluating brand elements such as logos, slogans, and messaging to ensure consistency and alignment with brand identity.
- Brand Tracking Studies: Monitoring brand metrics over time to gauge changes in brand perception and performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Brand Awareness: Measure of how well consumers recognize and recall the brand.
- Brand Loyalty: Assessment of customer retention and repeat purchase behavior.
- Brand Associations: Identification of strong and unique brand associations in the minds of consumers.
- Brand Sentiment: Analysis of consumer sentiment towards the brand, whether positive, negative, or neutral.
Challenges and Limitations
- Subjectivity: Brand equity measurement can be influenced by personal biases and perceptions, impacting the accuracy of results.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring that the data collected for brand equity measurement is reliable and representative of the target audience.
- Changing Market Dynamics: Brand equity can fluctuate due to changes in market conditions, consumer preferences, and competitive landscape.