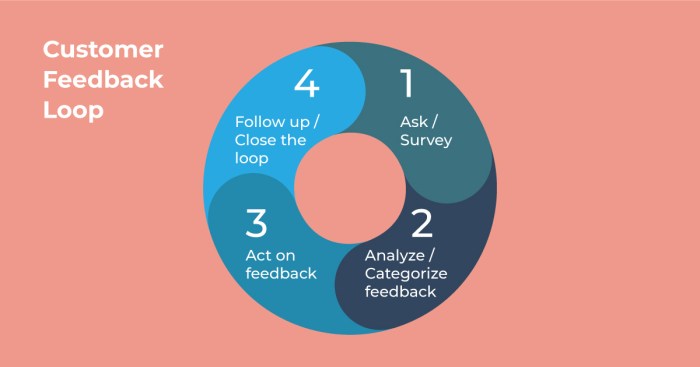
Building a Customer Feedback Loop sets the stage for companies to thrive by harnessing valuable insights from their customers. This essential process not only boosts customer satisfaction but also drives business growth in a competitive market.
Exploring the intricacies of feedback collection, analysis, and implementation, this journey empowers businesses to adapt, innovate, and excel in meeting customer needs and expectations.
Introduction to Building a Customer Feedback Loop
A customer feedback loop is like the secret sauce for a business, you know? It’s all about collecting, analyzing, and acting on feedback from customers to improve products and services. Super important stuff, man!
Having a well-established feedback loop can be a game-changer for a company, fo’ real. It helps businesses understand what customers dig and what they don’t, so they can make the necessary changes to keep everyone happy and coming back for more.
Creating Effective Feedback Channels: Building A Customer Feedback Loop
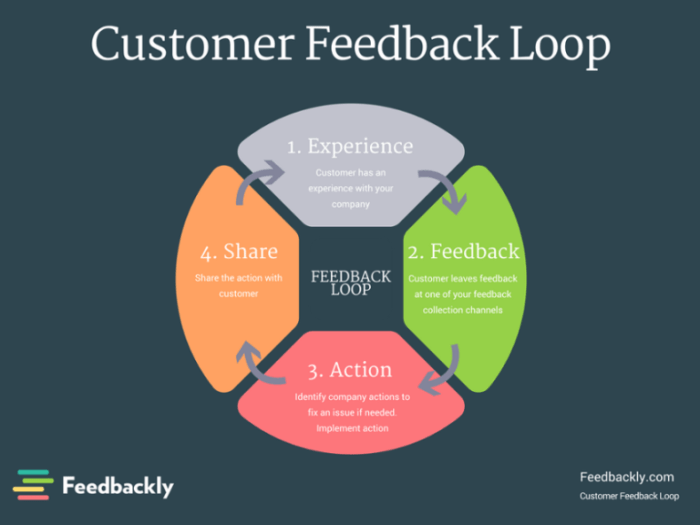
In the process of building a customer feedback loop, it is crucial to establish effective feedback channels to gather valuable insights from your customers. Different channels can be utilized to collect feedback, each with its own set of pros and cons in terms of accessibility and reliability.
Surveys
Surveys are a popular tool for collecting customer feedback as they allow for structured data collection and analysis. They can be distributed through various platforms such as email, websites, or even in-person. Surveys provide a direct way to gather specific information from customers, but they can be time-consuming to create and may not always capture detailed feedback.
Social Media
Social media platforms offer a more informal and immediate way to connect with customers and gather feedback. Through comments, messages, and polls, businesses can engage with their audience in real-time. However, the feedback received on social media may not always be comprehensive or representative of the entire customer base.
Emails
Emails are another common channel for collecting customer feedback, providing a direct line of communication between businesses and customers. Feedback forms or links to surveys can be included in emails to solicit responses. While emails offer a personalized approach, they may not always reach all customers or prompt immediate feedback.
In-Person Feedback
In-person feedback, such as through focus groups or customer interviews, can provide valuable qualitative insights. This channel allows for in-depth conversations and observations that may uncover hidden feedback. However, it can be time-consuming and may not always be feasible for all businesses.
Website Feedback Forms
Website feedback forms embedded on a company’s site can capture feedback from visitors in real-time. These forms can be strategically placed on key pages to gather specific feedback on user experience and satisfaction. While website feedback forms offer convenience, they may not capture feedback from all visitors.
Phone Surveys
Phone surveys involve directly calling customers to gather feedback on their experiences. This channel allows for a more personal touch and immediate responses. However, phone surveys can be intrusive and may not always yield high response rates.
Pros and Cons Summary
- Surveys: Structured data collection but may lack detailed feedback.
- Social Media: Immediate interaction but feedback may not be comprehensive.
- Emails: Direct communication but may not reach all customers.
- In-Person Feedback: Qualitative insights but can be time-consuming.
- Website Feedback Forms: Real-time feedback but may not capture all visitors.
- Phone Surveys: Personal touch but can be intrusive with lower response rates.
Analyzing and Organizing Feedback Data
When it comes to building a customer feedback loop, analyzing and organizing feedback data is crucial for extracting valuable insights that can drive business growth and improve customer satisfaction.
Process of Analyzing Feedback Data
Analyzing feedback data involves examining the feedback collected from customers to identify patterns, trends, and key insights. This process helps businesses understand customer preferences, pain points, and areas for improvement. Some methods for analyzing feedback data include:
- Utilizing text analysis tools to categorize and sentiment analysis to understand customer sentiments.
- Creating visualizations such as charts and graphs to identify trends and patterns in the feedback data.
- Segmenting feedback data based on various criteria like demographics, purchase history, or feedback source to gain deeper insights.
- Identifying common themes or s in the feedback to prioritize areas for improvement or innovation.
Methods for Organizing Feedback Data
Organizing feedback data efficiently is essential for further analysis and action planning. Some effective methods for organizing feedback data include:
- Utilizing a centralized feedback management system to store and categorize feedback data in one place.
- Tagging feedback with relevant s or categories for easy retrieval and analysis.
- Creating a feedback dashboard to track key metrics and visualize feedback data in real-time.
- Implementing a feedback scoring system to prioritize feedback based on importance and impact on customer satisfaction.
Implementing Changes Based on Feedback
Feedback from customers is a valuable source of information for companies looking to improve their products and services. Implementing changes based on this feedback can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business success. Let’s explore how companies have successfully utilized customer feedback to drive meaningful changes.
Example: Starbucks, Building a Customer Feedback Loop
- Starbucks received feedback from customers requesting more dairy-free milk options.
- As a result, they introduced almond milk and coconut milk to their menu.
- This change not only satisfied existing customers but also attracted new customers with dietary restrictions.
Example: Amazon
- Amazon implemented a feature that allows customers to easily track their orders in real-time.
- This change was based on feedback indicating a desire for more transparency and control over the delivery process.
- The new feature improved customer experience and reduced inquiries related to order status.
The Importance of Prioritizing and Acting on Feedback
Feedback can come in various forms and volumes, making it crucial for companies to prioritize and translate it into actionable steps. Here’s why this process is essential for continuous improvement:
Translating Feedback into Action
- Feedback alone is not enough; companies must analyze and interpret it to identify key areas for improvement.
- By translating feedback into actionable steps, companies can address specific issues and enhance overall customer experience.
Priority Setting
- Not all feedback carries the same weight or impact on customer satisfaction.
- Companies should prioritize feedback based on urgency, frequency, and potential impact on the business.
- Addressing critical feedback first can lead to quick wins and immediate improvements in customer relations.
Monitoring and Measuring Feedback Loop Success
In order to ensure the success of a feedback loop, it is crucial to monitor and measure its effectiveness. Key performance indicators (KPIs) play a significant role in evaluating the performance of a feedback loop and making necessary adjustments for optimal results.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Feedback Response Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of customers who provide feedback in response to requests. A higher response rate indicates active engagement and interest in providing feedback.
- Feedback Resolution Time: This KPI tracks the time taken to address and resolve customer feedback. A shorter resolution time indicates efficient handling of feedback and improved customer satisfaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty and satisfaction by asking customers how likely they are to recommend the product or service to others. A higher NPS indicates a stronger customer advocacy.
Monitoring and Adjusting Feedback Loop
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of the feedback loop are essential to ensure its effectiveness and relevance.
- Regularly review feedback data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Seek feedback from internal stakeholders to gain different perspectives on the feedback loop’s performance.
- Implement feedback loop enhancements based on data analysis and stakeholder input to optimize results.
Tools and Technologies for Managing Customer Feedback
When it comes to managing customer feedback, businesses have a variety of tools and technologies at their disposal to collect and analyze valuable insights. These tools help businesses make informed decisions and improve customer satisfaction.
Popular Tools for Collecting and Analyzing Customer Feedback
- SurveyMonkey: A popular online survey tool that allows businesses to create customized surveys to gather feedback from customers.
- Zendesk: A customer service platform that not only helps in managing customer inquiries but also collects feedback through various channels.
- Google Forms: A free tool by Google that enables businesses to create surveys and collect responses in an organized manner.
Comparison of Feedback Management Systems
| Feedback Management System | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| SurveyMonkey | Customized surveys, analytics, and reporting tools | Offers free basic plan with paid options for advanced features |
| Zendesk | Multi-channel support, ticketing system, feedback collection | Subscription-based pricing depending on the number of agents |
| Google Forms | Simple survey creation, integration with Google Sheets for data analysis | Completely free to use for all users |