Product Pricing Strategies set the stage for business success, determining how companies position their products in the market to drive sales and revenue. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced techniques, this topic delves into the intricate world of pricing strategies.
As we uncover the various factors influencing pricing decisions and delve into common strategies utilized by successful companies, you’ll gain valuable insights into the art of pricing products strategically.
Definition of Product Pricing Strategies

Product pricing strategies refer to the methods and techniques used by businesses to set prices for their products or services. These strategies are essential in determining the value of a product in the market and influencing consumer behavior.
Types of Product Pricing Strategies
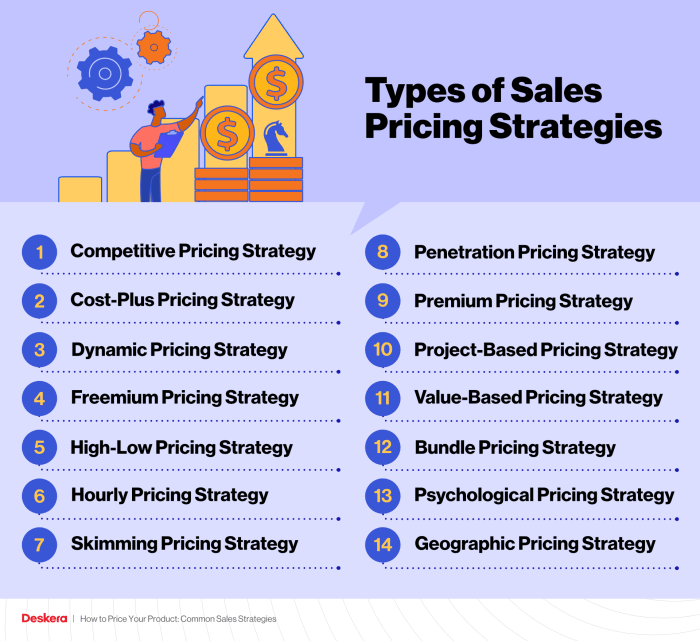
- Penetration Pricing: Setting a low initial price to attract customers and gain market share quickly.
- Price Skimming: Setting a high price initially and gradually lowering it as demand decreases.
- Value-Based Pricing: Setting prices based on the perceived value of the product to the customer.
- Competitive Pricing: Setting prices based on the prices of competitors in the market.
Impact of Effective Product Pricing Strategies
Effective product pricing strategies can have a significant impact on sales and revenue for a business. By pricing products strategically, companies can attract more customers, increase market share, and maximize profits. Additionally, the right pricing strategy can help businesses differentiate themselves from competitors and build brand loyalty.
Factors Influencing Product Pricing: Product Pricing Strategies
When determining the price of a product, several factors come into play that can greatly influence pricing decisions. These factors include market demand, competition, production costs, and target customer segments. Additionally, perceived value and pricing psychology also play a crucial role in setting the right price for a product.
Market Demand
Market demand refers to the level of desire consumers have for a particular product at a given price. The higher the demand for a product, the more a company can charge for it. Understanding market demand is essential for pricing strategies as it helps businesses set prices that customers are willing to pay.
Competition
Competitive pricing is a key factor in determining the price of a product. Companies need to consider the prices set by their competitors when deciding on their own pricing strategy. Being aware of competitor pricing can help businesses position their products effectively in the market.
Production Costs
Production costs play a significant role in product pricing. Businesses need to cover their costs to ensure profitability. Factors such as raw materials, labor, overhead costs, and any other expenses incurred in the production process need to be considered when setting prices.
Target Customer Segments, Product Pricing Strategies
Understanding the target customer segments is crucial for pricing decisions. Different customer segments may have varying price sensitivities and willingness to pay. Companies need to tailor their pricing strategies to appeal to their specific target market and maximize revenue.
Perceived Value and Pricing Psychology
Perceived value and pricing psychology influence how customers perceive the value of a product relative to its price. Businesses can use pricing strategies such as premium pricing, bundle pricing, and psychological pricing to influence customer perceptions and increase sales.
Common Pricing Strategies
In the world of business, pricing strategies play a crucial role in determining the success of a product or service. Different approaches are used by companies to set prices, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing is a straightforward strategy where a company calculates the cost of producing a product and adds a markup to determine the selling price. This markup ensures that the company covers its costs and generates a profit. While this method is easy to implement and provides a guaranteed profit margin, it may not take into account market demand or competition.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product or service to the customer. Companies using this strategy set prices based on how much customers are willing to pay for the benefits they receive. This approach allows for higher prices for products with unique features and strong brand loyalty but requires a deep understanding of customer preferences.
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to quickly gain market share. This strategy is often used for new products to attract customers and build a customer base. While penetration pricing can lead to rapid adoption and brand awareness, it may not be sustainable in the long run if prices need to be increased later.
Skimming Pricing
Skimming pricing is the opposite of penetration pricing, where a high initial price is set to maximize profits from early adopters willing to pay a premium. Over time, the price is gradually lowered to attract more price-sensitive customers. This strategy allows companies to capture maximum revenue from different customer segments but may limit market penetration.
Dynamic Pricing and Personalized Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a strategy where companies adjust prices in real-time based on various factors such as demand, competition, and even time of day. This allows businesses to optimize their pricing to maximize profits and stay competitive in the market.
Benefits of Dynamic Pricing:
Dynamic pricing helps companies increase revenue by adjusting prices based on demand fluctuations. It also allows businesses to stay competitive and react quickly to market changes.
Challenges of Personalized Pricing:
Personalized pricing based on customer data and behavior can lead to concerns about privacy and fairness. It also requires sophisticated data analysis and technology to effectively implement.
Examples of Companies Using Dynamic or Personalized Pricing:
- Amazon: Amazon adjusts prices for products based on factors like demand, competitor prices, and customer browsing history.
- Uber: Uber uses dynamic pricing to adjust ride fares based on factors like time of day, traffic conditions, and demand for rides.
- Netflix: Netflix offers personalized pricing plans based on user preferences and viewing habits to cater to individual needs.